Table of Content
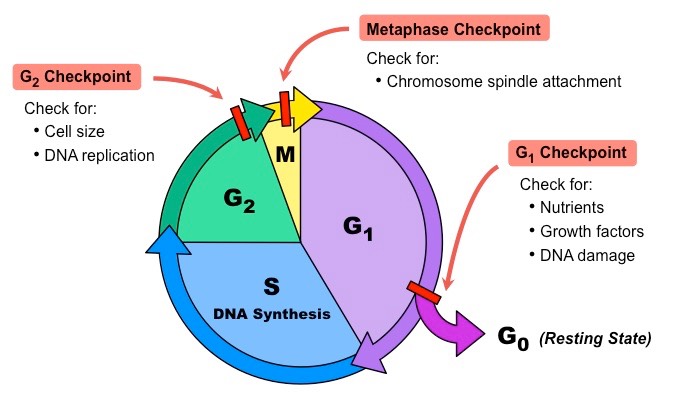
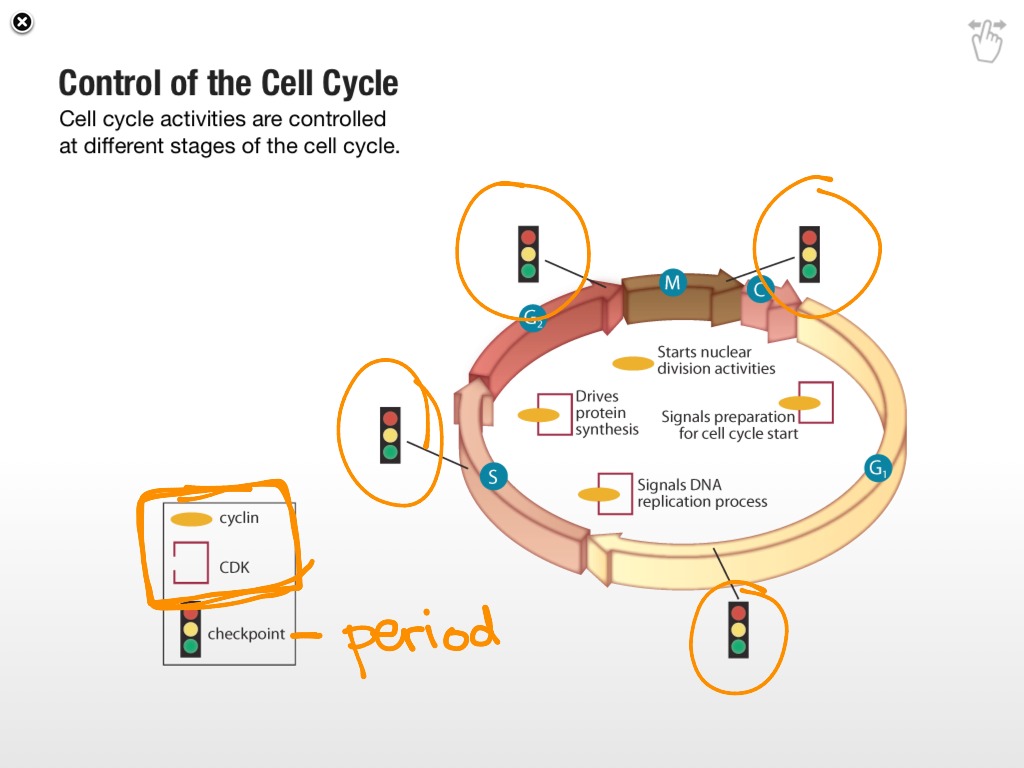
Internal factors kinases change the activity of other molecules by adding a phosphate group cyclins ... - KEY CONCEPT Cell cycle regulation is necessary for healthy development. 5.A checkpoint in the cell cycle is a important control point the place stop and go signals regulate the cycle. three major checkpoints are discovered in the G1, G2, and M phases. The cell cycle begins when the cell is shaped and ends when the cell divides and types new cells. Or growth previous to cell division.
Regulation of mitotic cyclin B levels in M-Phase The anaphase-promoting complex is activated solely when MPF activity is excessive. Binding of the active APC and E2 covalently linked to a ubiquitin to the cyclin B destruction box leads to the addition of a number of ubiquitin molecules. As the polyubiquitinated cyclin B is degraded, MPF activity declines, triggering the onset of telophase. Following cytokinesis, synthesis of cyclin B occurs in the interphase daughter cells. APC exercise remains high till late in the G1 of the following cell cycle when it's inactivated by a G1 Cdk complicated.
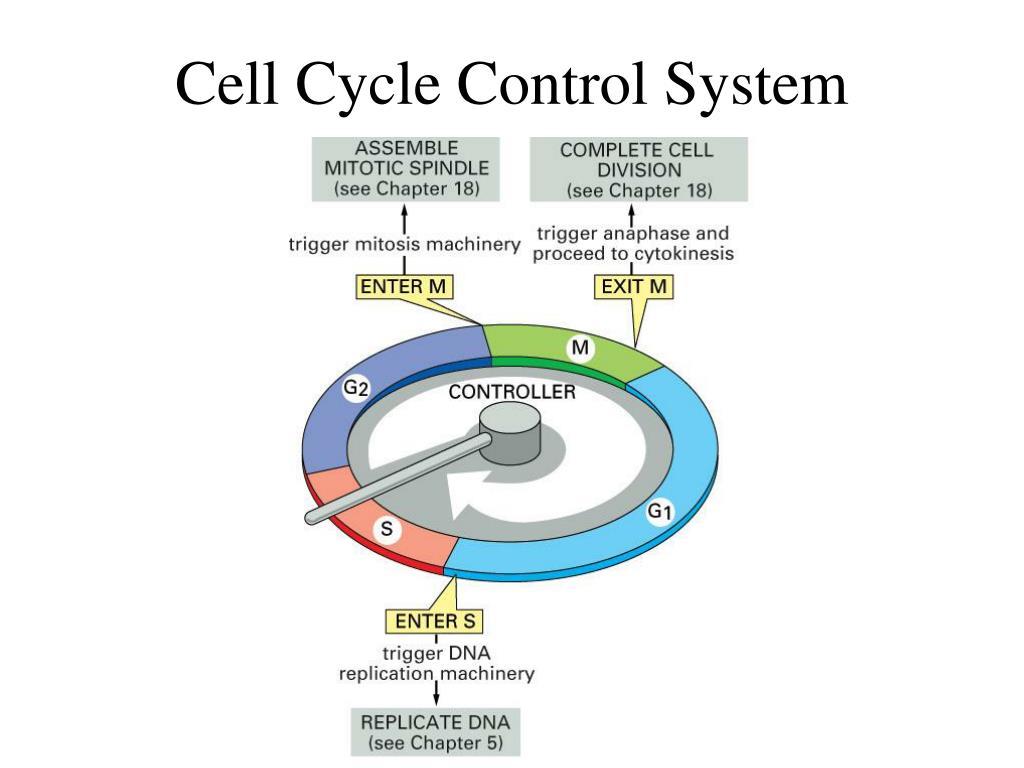
Cell Cycle Regulation
A cell accommodates all the data essential for making a duplicate of itself throughout ... Disassembly of the mitotic spindle. Cell Cycle Regulation - A cell incorporates all the information necessary for making a copy of itself during ... Cell Cycle Checkpoints - . They monitor the cell cycle before it can proceed to the following stage. 9.G1 checkpoint • Controlled by G1 Cdks-cyclin • G1 cyclin levels additionally vary with the cell cycle • Many additional levels of phosphorylation, dephosphorylation regulate.
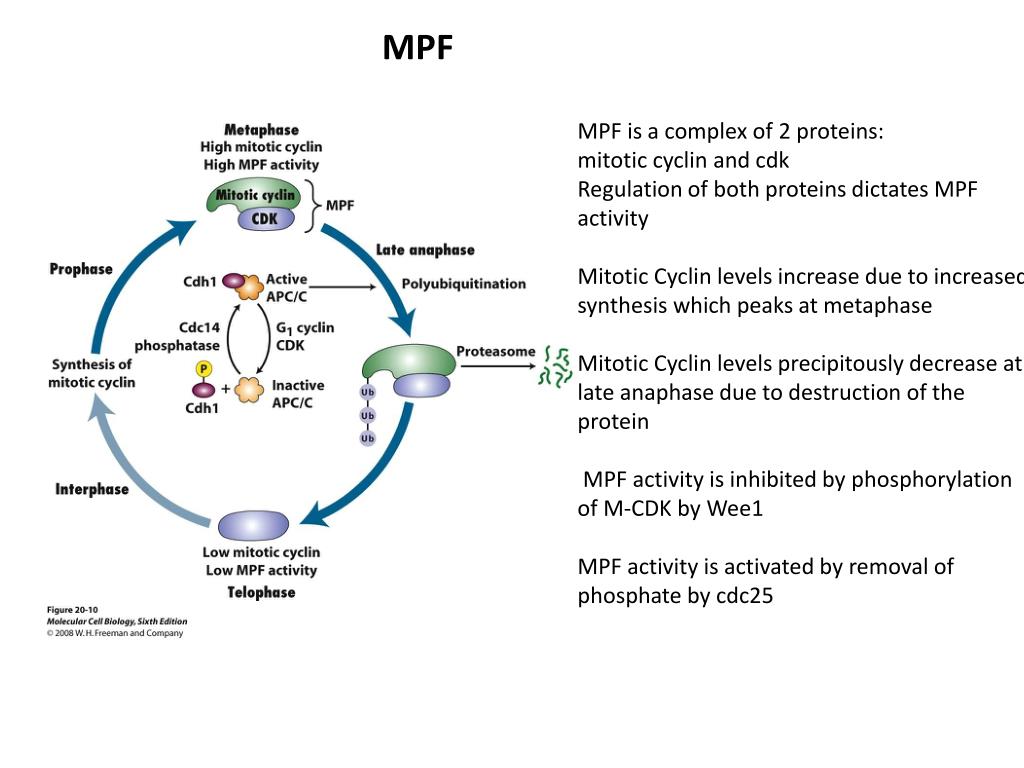
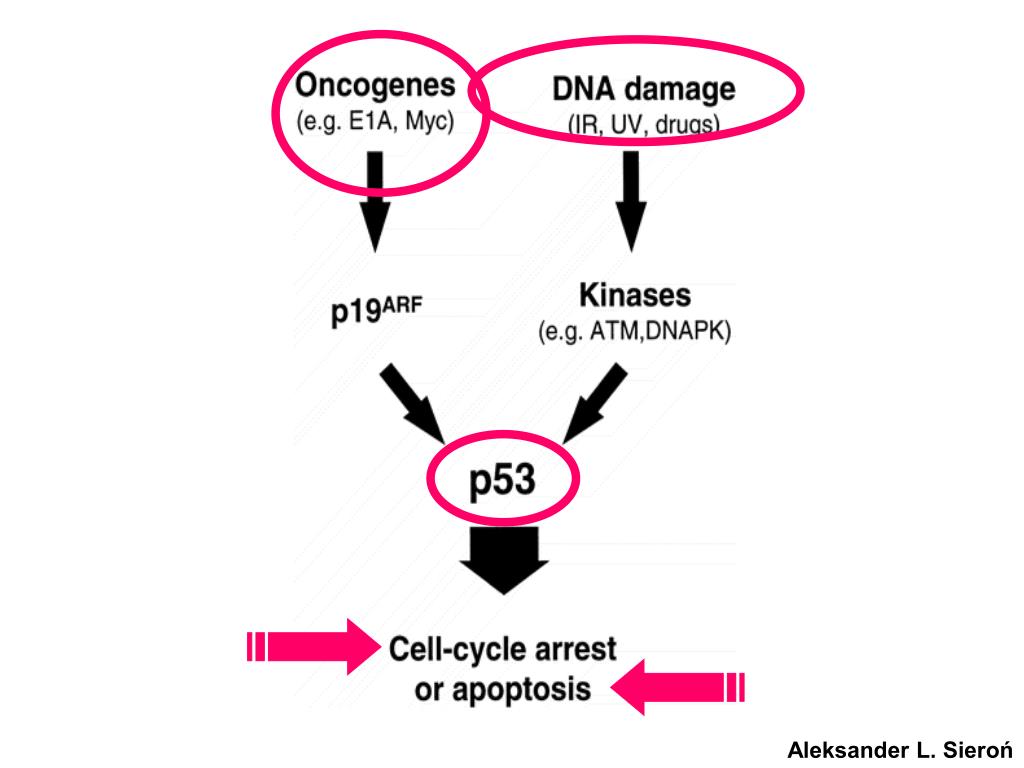
2. Two elementary processes happen with each cell cycle--chromosomes replicate, after which they segregate equally to two daughter cells. The mechanisms by which these processes occur are comparable in all eukaryotic cells. Processes occurring in the course of the cell cycle are extremely regulated and coordinated. The cell cycle is regulated primarily at the DNA replication and mitosis steps. P53-induced cell-cycle arrest in response to DNA damage The usually unstable p53 protein is stabilized by broken DNA, so its concentration will increase. Acting as a transcription factor, p53 induces expression of p21CIP, a cyclin-kinase inhibitor that inhibits all Cdk1-, Cdk2-, Cdk4-, and Cdk6-cyclin complexes.
Cell Cycle Regulation
These mechanisms aren't current in all cell varieties; many are lacking in early embryonic cell cycles, for example. Mechanisms controlling S-phase initiation in animal cells G1-Cdk activity (cyclin D-Cdk4) initiates Rb phosphorylation. This inactivates Rb, liberating E2F to activate the transcription of S-phase genes, including the genes for a G1/S-cyclin and S-cyclin . The ensuing appearance of G1/S-Cdk and S-Cdk actions further enhances Rb phosphorylation, forming a positive suggestions loop. E2F acts back to stimulate the transcription of its own gene, forming another optimistic feedback loop. E2F as a progress Promoter E2F is a transcription factor that activates several replication and development related genes.
Ensures daughter cells don't end up with lacking or additional chromosomes. Kinetochores that have not connected to spindle microtubules sign to delay anaphase. However, cells aren't destroyed proliferate to form a tumor - a mass of abnormal cells. If the irregular cells stay on the originating web site, the lump is called a benign tumor.
Assist Us Hold Slideshare Free
Oxygen and food move into cells, whereas waste products transfer out of cells. How does the size of a cell affect how effectively materials get to all elements of a cell? Work with a companion to complete - Work with a associate to complete this exercise.
Classify Cells relative to. Cell Cycle Phase hyperlink ... Cell Cycle and Cell Division - ... Getting Through Materials transfer through cells by diffusion.
Alter mobile functions ... Behave in another way relying upon cell kind from which originate ... Normal genes that if mutated might act to make a cell cancerous ... Cell Cycle Regulation and Cancer - Alter mobile functions ... A single cell escapes from the regulation of its own division ... Allium root tip a mitosis classic!
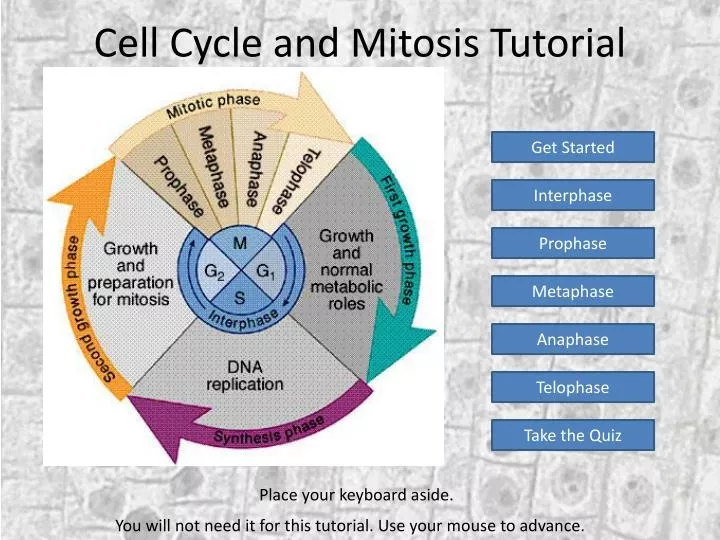
Involves the distribution of genetic material from parent to daughter cell Functions copy of a whole ... The Cell Cycle - Described by Rudolf Virchow in 1855. The centrosome determines the airplane of cell division. It doubles throughout S phase and will determine the spindle orientation. Each centrosome can consist ... eleven THE CELL CYCLE AND CELL DIVISION - segregation.
Just Like Cell Cycle Regulation Ppt (
Cell Phase Specific Cyclins Activity of mammalian Cdk-cyclin complexes via the course of the cell cycle in G0 cells induced to divide by remedy with growth elements. The width of the colored bands is approximately proportional to the protein kinase exercise of the indicated complexes. Cyclin D refers to all three D-type cyclins.
(which controls the cell's activities) in a single cell can solely achieve this much at a time ... Cell Cycle Regulation and Checkpoints. Cell division cycle has 4 basic steps. Interphase G1 S G2 Mitosis. G1 part S Phase G2 Mitosis Each of those steps has a number of ranges of regulation to forestall errors from occuring.
During G0/G1 transition, E2F is bound to activated or unphosphorylated RB, and as a consequence is unable to activate transcription. The RB-E2F complicated may be disrupted by phosphorylation of RB or by DNA viral oncoproteins that bind RB. The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle In most rising cells, the 4 phases proceed successively, taking from hours relying on cell sort and developmental state. Interphase comprises the G1, S, and G2 phases. DNA is synthesized in S, and different cellular macromolecules are synthesized throughout interphase, so the cell roughly doubles its mass.
Instant access to hundreds of thousands of ebooks, audiobooks, magazines, podcasts and extra. The SlideShare family just obtained greater. Enjoy entry to tens of millions of ebooks, audiobooks, magazines, and more from Scribd.
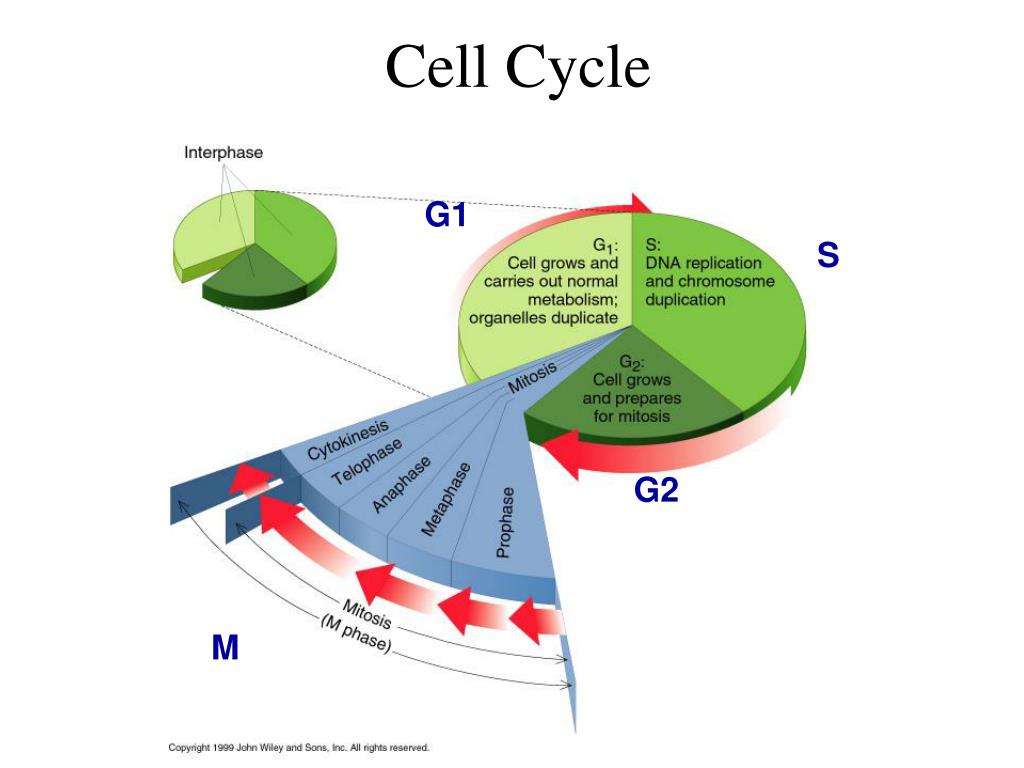
Cell Cycle
During G2 the cell is ready for the mitotic part, when the genetic materials is evenly partitioned and the cell divides. Nondividing cells exit the conventional cycle, getting into the quiescent G0 state. The cell cycle and cell division Why is it known as the cell cycle?